Disclaimer: Educational content only. This compound lacks FDA approval for human use and is classified as FDA Category 2. Not medical advice. Consult a physician for health decisions. Imagine if your cells had a reset button. A way to wind back the genetic clock that dictates how fast you age, how well you sleep, and how quickly you recover. For decades, this “reset button” was a state secret of the Soviet Union, used to keep cosmonauts healthy in the radiation of space
Today, it’s known as Epitalon (or Epithalon), and for many biohackers, it represents the closest science has come to bottling time.
But if you are searching for this peptide, you are probably confused. Is it “Epitalon” or “Epithalamin”? Is it legal? What does the research actually show?
This guide cuts through the noise. We bridge the gap between rigorous Russian science and practical understanding, covering what researchers have found, the FDA’s 2024 classification, and the quality standards that matter.
What Is Epitalon? (And What It Isn’t)
First, let’s clear up the biggest source of confusion: the name.
Epitalon is a synthetic tetrapeptide. That means it is a precise chain of just four amino acids: Alanine, Glutamate, Asparagine, and Glycine (AEDG).
Developed by Professor Vladimir Khavinson at the St. Petersburg Institute of Bioregulation and Gerontology. Khavinson originally worked with Epithalamin, a crude extract taken from the pineal glands of young calves. While Epithalamin showed promise in animal trials, extracting peptides from cattle is messy, inefficient, and difficult to standardize.
Khavinson identified the active “pharmacophore,” the specific sequence causing the effect, and synthesized it. The result was Epitalon.
- Epithalamin: Natural, bovine extract, complex mixture.
- Epitalon: Synthetic, precise, 4-amino acid chain.
The Bottom Line: When you see a vial online today, you are almost certainly looking at Epitalon (the synthetic version), not the bovine extract.
The Science: Why We Age (The Shoelace Analogy)
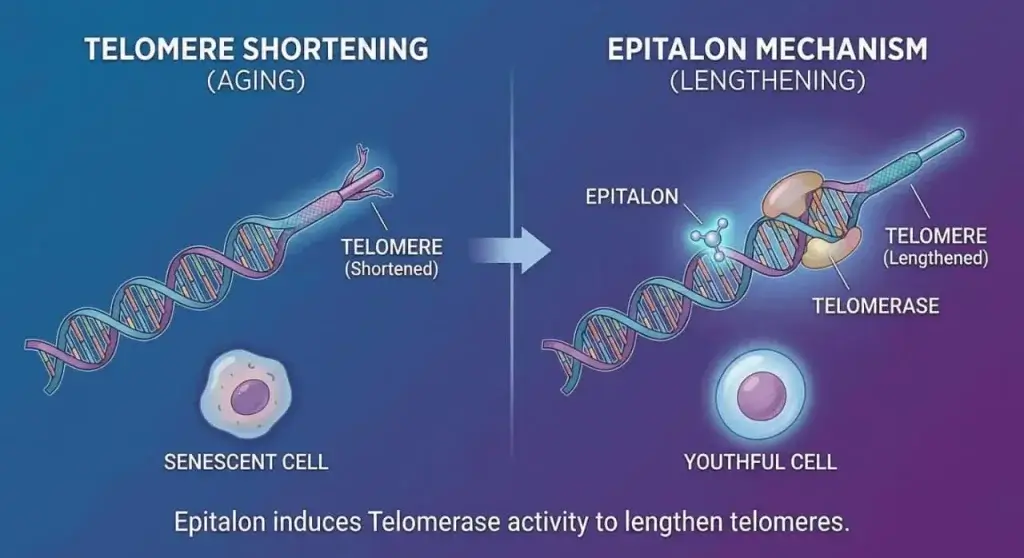
To understand why Epitalon is called the “longevity peptide,” you have to understand telomeres.
Think of your DNA strands like shoelaces. At the end of every shoelace, there is a plastic cap called an aglet that keeps the lace from fraying. In your cells, these caps are called telomeres.
Every time your cells divide, those telomeres get a little shorter. Eventually, they get so short that the cell senses damage and stops dividing (senescence) or dies. This limit is the cellular “clock” of aging.
How Researchers Believe Epitalon Works
Epitalon appears to act as a gene switch. Research suggests it enters the nucleus and binds to specific DNA sequences to induce telomerase activity. Telomerase is an enzyme that adds DNA repeats back to the telomeres, effectively lengthening them.
Unlike gene therapy, which alters your DNA, Epitalon is believed to work epigenetically. It uncoils the DNA structure to allow the cell to read instructions that were previously inaccessible.
What Research Has Examined
The Russian data on this peptide is extensive. Long-term studies by Khavinson examined elderly patients treated with pineal peptides, observing differences in mortality rates compared to controls. Here’s what researchers have investigated:
Sleep and Circadian Research
This is often the first area of interest. Epitalon research has examined pineal gland function and endogenous melatonin production.
Important Distinction: Taking a melatonin supplement can downregulate the body’s own production. Researchers have explored whether Epitalon works differently by supporting the gland’s natural function rather than replacing the hormone.
Skin and Cellular Research
There is a reason “epitalon for skin” appears in searches. By potentially affecting the telomeres of fibroblasts (skin cells responsible for collagen), researchers have examined effects on cellular aging in skin tissue.
The Cancer Question
This is the most sensitive topic. Since telomerase is active in many cancers, does activating it cause cancer?
The Research Direction: Animal studies by Khavinson’s team observed a reduction in spontaneous tumor incidence. The hypothesis is that Epitalon may elongate telomeres in healthy cells to prevent genomic instability (itself a cause of cancer).
Critical Precaution: Despite this research direction, the compound is strictly contraindicated for anyone with active cancer or cancer history. Consult an oncologist before considering any telomerase-related compounds.
Regulatory Status: The 2024 Shift
The landscape shifted dramatically in 2024.
FDA Classification: Epitalon was placed on the FDA’s Category 2 list of bulk drug substances. This means US compounding pharmacies can no longer legally compound Epitalon for patients.
The Consequence: The prescription pathway closed. What remains is the grey market of “research chemicals.”
This is not a minor regulatory footnote. It reflects the FDA’s position that insufficient safety data exists for human therapeutic use.
Quality Standards for Research Compounds
Since the market operates in a grey zone, quality verification matters enormously.
What to look for:
- Certificate of Analysis (COA) from independent labs
- Purity verification of 99% or higher
- Batch-specific documentation (not generic PDFs)
- Proper storage and cold-chain shipping
Red flags:
- Prices dramatically below market
- No COA available on request
- Recycled or generic documentation
- Vendors with FDA warning letters
The peptide market has no regulatory oversight. Due diligence is the only protection.
The Philosophical Shift: Restoration vs. Replacement
Western medicine often focuses on replacement. Low thyroid? Take thyroid hormones. Low testosterone? Take testosterone.
Epitalon represents a different research direction: restoration. The hypothesis is not about replacing a hormone but about supporting the gland that produces the hormone.
It is “teaching a man to fish” vs. “giving a man a fish.”
Whether this paradigm proves out in rigorous human trials remains to be seen. The preclinical research is intriguing. The long-term human data is still developing.
The Bottom Line
Epitalon bridges Soviet-era research and modern longevity science. The mechanistic theory is compelling. The animal data is extensive. The human clinical evidence remains limited.
This compound is:
- FDA Category 2 (cannot be compounded)
- Not approved for any therapeutic use
- Available only as a research chemical
- Contraindicated for anyone with cancer history
The telomere science is fascinating. The practical applications for humans remain unproven by Western clinical standards.
Anyone interested in this compound should understand both what the research shows and what remains unknown. Consult healthcare providers familiar with the current literature before making any decisions.
References
Khavinson Telomerase Research Khavinson VK, et al. “Peptide Regulation of Gene Expression and Protein Synthesis in Bronchial Epithelium.” Lung. 2014.
Telomere Biology Blackburn EH, et al. “Telomeres and telomerase: the path from maize, Tetrahymena and yeast to human cancer and aging.” Nat Med. 2006.
Pineal Peptides and Aging Khavinson V, Morozov V. “Peptides of pineal gland and thymus prolong human life.” Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 2003.
FDA Category 2 Designation FDA Pharmacy Compounding Advisory Committee, 2024. in history—bridging the gap between Soviet secrets and modern biotechnology.
Is epithalon legal?
Epithalon is generally sold as a research peptide.
That means:
It’s not FDA-approved for anti-aging or disease treatment.
Rules vary by country and region.
Will epithalon make me live longer?
We have animal data suggesting longer lifespan and fewer tumors.
Human data showing better aging markers and function when using pineal peptides like epithalamin.
Can you take epithalon orally?
Epithalon is usually discussed as:
Injectable (IM or SubQ) in the medical literature.
Oral peptides are tricky because your gut breaks them down like food. Some companies may sell oral or sublingual versions, but bioavailability is questionable and not as well documented as injections.
If your doctor suggests an alternative route, you talk through pros/cons with them.
Is it safe to stack epithalon with other peptides?
Depends on:
Your health status
Current medications
What other peptides you’re using (GH secretagogues, TB4, BPC-157, etc.)
Stacking can make sense in a structured protocol guided by lab work and a practitioner.
DIY stacking because someone on YouTube looked jacked? Hard pass.